In this tutorial we will find out how to create a first version of a REST API application using Spring Framework. This application will be later extended with more features like database storage, tools for documentation, client guidance and others features.
For now, we want to keep things clear and simple with the most basic REST API we can create.
A REST API is a way for different computer systems to communicate with each other over the internet using HTTP protocol (the same protocol used for websites) and applying the same set of predefined communication rules with the same data format (usually JSON).
When we are talking about REST APIs, we are thinking at a list of resources. The “thing” you’re dealing with (like a user, product, or order) is called a “resource.”
Resources are usually represented as URLs (example https://api.example.com/api/lemonades) and the actions on the resources are defined by some standard HTTP Methods:
REST APIs typically use JSON to send and receive data because it’s easy for both humans and machines to read and each request from the client contains all the information needed. The requests are independent and the server doesn’t remember past interactions.
Let’s check an example:
A client (a web or a mobile application): Give me the list of lemonades
The server (our REST API application): here you have the list
Which is translated to:
A client calls: GET https://api.example.com/api/lemonades
The server response:
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Sweet lemonade",
"description": "cold and sweet"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Lemonade shot",
"description": "short and fresh"
}
]
Spring Boot is an excellent choice for creating REST APIs because it simplifies the process, provides powerful features, and is designed for speed and scalability. Also it includes an embedded server (in our case Tomcat) so you can run your REST API immediately without installing external web servers.
Spring Boot is widely used in the industry, so it’s easy to find documentation, tutorials, and community support.
We created an introductory tutorial to Spring Boot and you can check it here.
You can use Spring Initializr to quickly generate a Spring Boot project with Maven or Gradle. We can use the following configurations:

You will receive a ready-to-use project. All the configurations are already written in the build.gradle file and the start ExplainjavaRestApiApplication class is already created.
Additionally, we also have an already created structure in the resources folder and a test package.
In the next step, we should create a package for each layer of our application: Domain, Repository, Service, Controller.
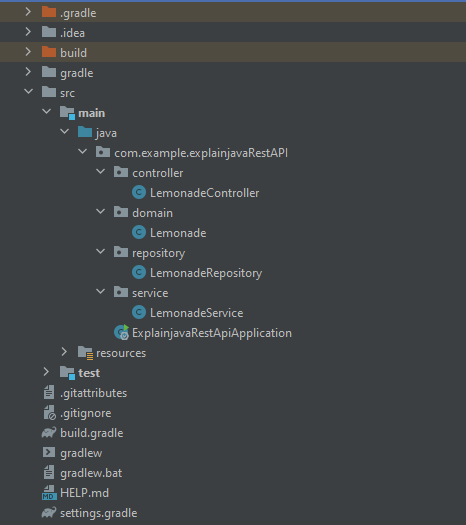
The goal of this tutorial is to create a REST API application to serve the resource “Lemonade” to clients. In order to do that, we will create a multi-layer application with an in-memory repository for storage and annotations based dependency injection:
public class Lemonade {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String description;
public Lemonade() {
}
public Lemonade(Long id, String name, String description) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
@Repository
public class LemonadeRepository {
private final Map<Long, Lemonade> lemonades = new HashMap<>();
public Lemonade save(Lemonade lemonade) {
lemonades.put(lemonade.getId(), lemonade);
return lemonade;
}
public Lemonade update(Long id, Lemonade updatedLemonade) {
if (lemonades.containsKey(id)) {
updatedLemonade.setId(id);
lemonades.put(id, updatedLemonade);
return updatedLemonade;
}
return null;
}
public void deleteById(Long id) {
lemonades.remove(id);
}
public List<Lemonade> findAll() {
return new ArrayList<>(lemonades.values());
}
public Optional<Lemonade> findById(Long id) {
return Optional.ofNullable(lemonades.get(id));
}
}
@Service
public class LemonadeService {
@Autowired
private LemonadeRepository lemonadeRepository;
public Lemonade createLemonade(Lemonade lemonade) {
return lemonadeRepository.save(lemonade);
}
public void deleteLemonade(Long id) {
lemonadeRepository.deleteById(id);
}
public Lemonade updateLemonade(Long id, Lemonade updatedLemonade) {
return lemonadeRepository.update(id, updatedLemonade);
}
public List<Lemonade> getAllLemonades() {
return lemonadeRepository.findAll();
}
public Optional<Lemonade> getLemonadeById(Long id) {
return lemonadeRepository.findById(id);
}
}
The final layer of our application is the RestController. It is the place where we can define our REST endpoints and methods. As we said before, we need to create the CRUD operations for our resource and for that, we need to define the following endpoints:
Spring allows us to create all these configurations using simple annotations as we can see in the following example:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/lemonades")
public class LemonadeController {
@Autowired
private LemonadeService lemonadeService;
@GetMapping
public List<Lemonade> getAllLemonades() {
return lemonadeService.getAllLemonades();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Lemonade> getLemonadeById(@PathVariable Long id) {
return lemonadeService.getLemonadeById(id)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.orElse(ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
@PostMapping
public Lemonade createLemonade(@RequestBody Lemonade lemonade) {
return lemonadeService.createLemonade(lemonade);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Lemonade> updateLemonade(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Lemonade updatedLemonade) {
Lemonade lemonade = lemonadeService.updateLemonade(id, updatedLemonade);
if (lemonade == null) {
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(lemonade);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteLemonade(@PathVariable Long id) {
lemonadeService.deleteLemonade(id);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}
When we start the application using bootRun command, we can see the Spring starting logs, a Tomcat server starts on the port 8080, and we can use Postman or cURL to test the API. When we type the GET URL in our browser, we receive an empty list of entities because our list is empty.
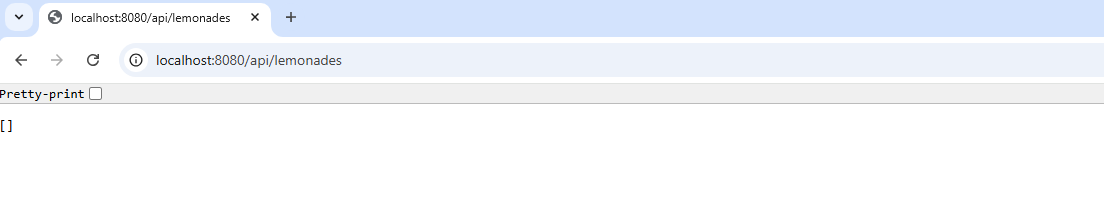
You can check our tutorial on testing the REST API using Postman to see how every operation works.
In this tutorial we created a basic REST API using Gradle and Spring Framework. We had a short introduction on what a REST API is and how to create an application to serve a resource. In the next tutorials we will improve our application by adding more features.
Learn advanced concepts, work on real-world projects, and fast-track your journey to becoming a proficient Java developer. Start now and unlock your full potential in the world of Java programming!
Start now and unlock your full potential in the world of Java programming!


The place where you can start your Java journey.
© All Rights Reserved.