In this final step of our chapter, we will summarize the steps you need to take when tackling this kind of problem. Additionally, we will suggest some similar Java project ideas to help you practice the concepts learned so far and we will discuss what your future development journey could look like.
Practicing with personal projects is one of the best ways to learn programming because it helps you apply what you’ve learned in real-world scenarios. Instead of just memorizing concepts, you get hands-on experience with problem-solving, debugging, and structuring code efficiently.
Beside all these arguments, if you’re looking for a job, personal projects serve as a great portfolio to showcase your skills to potential employers.

Because we believe that practice is essential, we have prepared some similar OOP Java project ideas to help strengthen all the concepts you have learned until now:
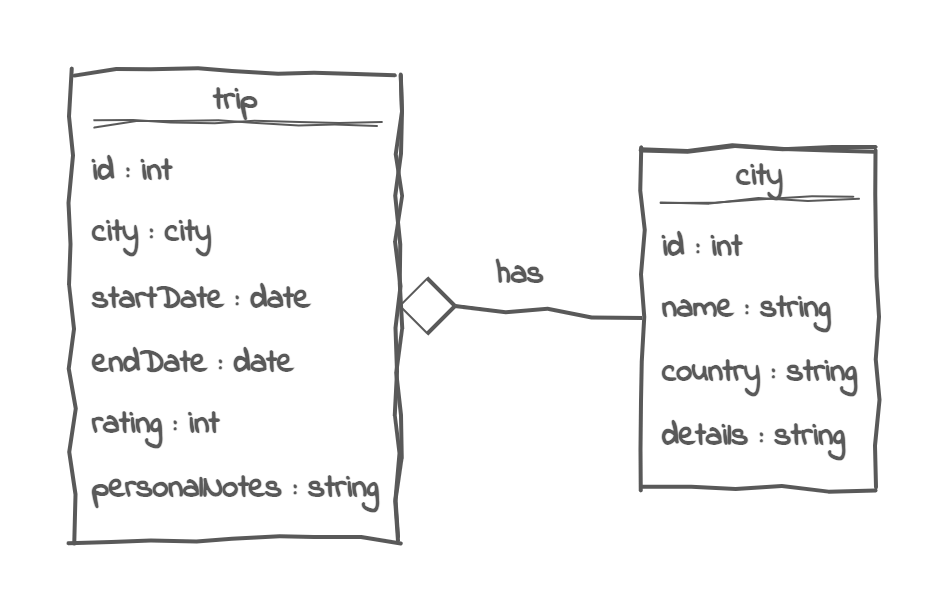
Create a project for a person who is passionate about traveling and wants to manage their city breaks effectively. The program helps the user track the cities they’ve visited, the destinations on their bucket list, and the trips they’ve taken, along with any highlights or personal notes.
First, the application should have a city entity which represents a city the traveler has visited or dreams of visiting. Each city has details like a name, country and details about its attractions (a string that contains some information about the city). For example, Paris might have a description like “vibrant culture, incredible food, must see the Louvre museum and the Eiffel Tower”. The user should have a menu to handle cities: add, update, delete, and show all the cities from the application.
The user can record trips they’ve taken, specifying the city they visited, start and end date of the trip, the rating of the trip and personal notes. In a city break, only one city can be visited. For example, the person who uses the application should be able to add Paris in the trip list that he already has and write the details about the trip. Besides saving the trip, the use should be able to update, delete and show all the trips.
Todo list:
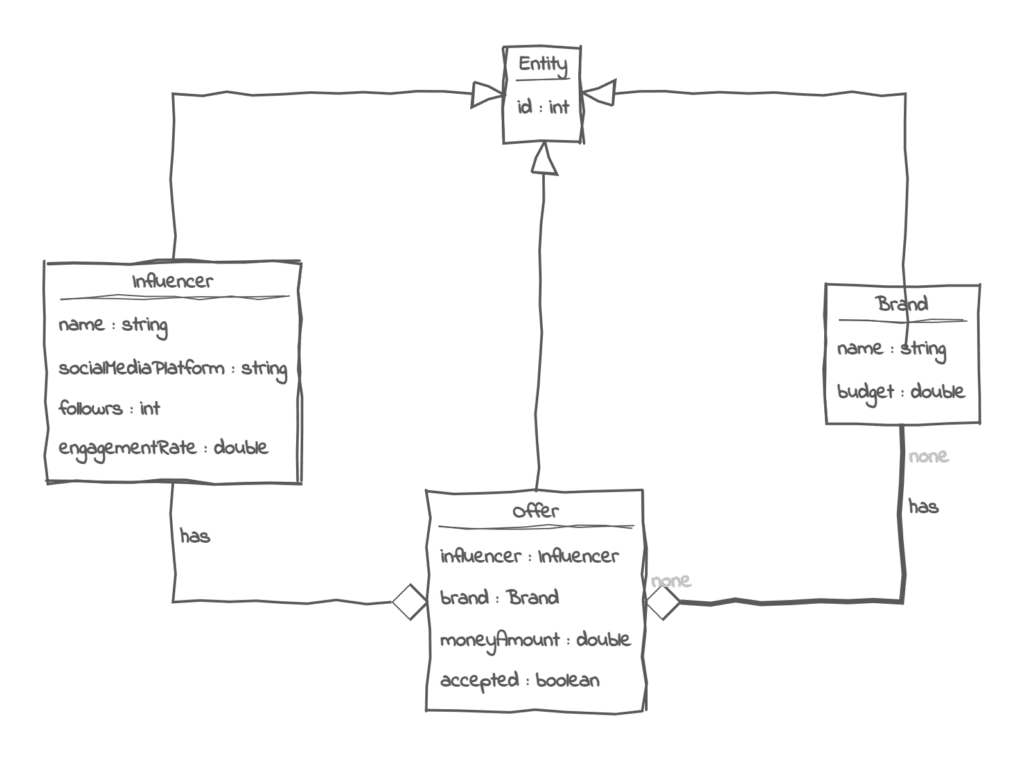
Create a system that allows brands to offer sponsorship deals to influencers based on their follower count and engagement rate. Influencers can accept or reject these offers, and the system keeps track of their total earnings and the remaining budget of brands.
The system should allow influencers to register their name, social media platform (TikTok, YouTube, Instagram, etc.), number of followers, engagement rate (percentage of followers who interact with their content) and brands with the name and a total budget.
The system should allow brands to create an offer for an influencer. When it is created, the brand should introduce the amount of money. By default, the offer is pending, but an influencer should see their offers and should be able to accept it. When accepted, the money is extracted from the brand budget.
Todo list:
Build a simple music streaming app like Spotify or Apple Music. In this app, users can play songs, organize them into playlists, explore albums, and discover artists. To create this system, you need to model different entities that represent the core parts of the app: songs, albums, artists, and playlists.
We need to start by defining a few core elements. First, a song represents a piece of music with a title and duration. Every song belongs to an album and can have one or more artists performing it. For example, a song like “Baby One More Time” might be performed by “Britney Spears” and could be part of the album “…Baby One More Time”.
An album is a collection of songs grouped together, often by the same artist. The album has a title, a release year, and contains multiple songs. For example, “…Baby One More Time” might include several tracks like “(You Drive Me) Crazy” and “Sometimes”, all performed by Britney Spears. The album allows users to view all the songs it contains, and we can also calculate the total length of the album by adding up the durations of each track.
An artist is the person or group that creates and performs music. Artists can release multiple albums and collaborate on various songs. For instance, Britney Spears might be a solo artist who has released “…Baby One More Time”, contributing to every song on the album. Artists also belong to different musical genres, such as pop or rock.
Finally, a playlist allows users to create custom lists of songs they enjoy. A playlist can contain multiple songs from different albums and artists. For instance, a user might create a playlist called “Favorites” and add “Sometimes” and “(You Drive Me) Crazy” to it. A song can be added to multiple playlists, and a playlist can have many songs.
When you open the app, all the artists, songs and albums should be loaded from text files. A user should be able to display all artists, songs and albums. In the same time, a user should be able to create, update or delete a playlist.
This application should have statistics as well. We need to find out who is the most added artist in the playlist (name and the number of songs in playlist) and top 5 albums by total songs length (artist name, album name and total length).
Todo list:
You have been tasked with developing a Food Waste Management System to help reduce the environmental impact of food waste. The purpose of this system is to track food donations, manage collection centers, and facilitate waste processing to ensure efficient and sustainable waste disposal. This system will monitor the key entities involved in the process, including food donors, collection centers, waste processors, and the types of waste they handle.
Food donors are sources that provide food waste, such as grocery stores, restaurants, and food distribution centers. Each donor should have a name, an address, and contact information. Donors can donate multiple food waste items over time. Additionally, each Food Donor can deliver waste to multiple collection centers.
Each food waste item represents a batch of food that has been donated and designated as waste. For each food waste item, the system should track its weight (in kilograms), the expiration date, and the type of waste (for example, vegetables, dairy, or grains). Each food waste item should belong to a specific food donor that provided it. However, food waste items may pass through various processors as they are collected and processed.
Collection centers are designated facilities that collect food waste from various donors before it is sent for processing. Each collection center should have a location, and a maximum capacity (measured in kilograms) to indicate how much waste it can hold. Each collection center can accept food waste from multiple donors. Once collected, food waste from each collection center is then sent to a specific waste processor.
For example, a collection center located near a city center may receive waste from multiple restaurants and grocery stores and send it to a processor that specializes in composting.
Processors are entities responsible for converting food waste into useful byproducts, such as compost, energy, or fertilizer. Each processor has a name, a location, and a maximum processing capacity to indicate how much waste it can handle. Each processor can handle food waste from multiple collection centers. When a food waste item arrives at one processor, the food waste item is marked as processed.
All day we need to wait at one collection center food donors and food waste items. At the end of the day, we need to send all the food waste to one processor. If the collection center is full of we cannot accept more food waste.
All data should be stored in files and validated when is saved.
At the end, we need to create some reports as well. We need to know who is the most active food donor and what type of waste is the most donated.
Todo list:

At the beginning of this course, we were presented with a real-world problem: a management system for a lemonade stand, where a user can manage suppliers, products, create lemonade recipes and sell them to customers.
To solve this problem, we created a multi-layer application using only plain Java, without any frameworks. The goal of this chapter was to explore how a multi-layered application should be designed, analyzed, and developed.
We used principles of Object-Oriented Programming to build a fully functional application. We covered topics such as testing, entity handling, exceptions and storage. Additionally, we utilized inheritance, interfaces, generics and many other Java features.
Before we started coding, we conducted a preliminary analysis step, similar to how software projects are handled in real life. We emphasized the importance of analyzing and planning everything before diving into the development of a software product.
Next, we managed the first entity in order to build the foundation of our multi-layer application. We explored each layer in detail: Repository, Service and UI.
Once the first version of our application was functional, we introduced testing – a crucial step in software development. We discussed key software testing principles used in real world projects.
Step by step, we added new functionalities in order to practice some Java features. These included data validation using exceptions and file storage using inheritance.
The next step was to improve our entity management by exploring relationships between entities. We worked on examples for one to many and many to many relationships.
To further improve our application, we abstracted our layers using other Java features: interfaces, generics and inheritance.
The business layer of our application was reinforced with a functionality which required different entities and more business logic: creating an order for our lemonade stand.
The final step of our application was generating reports, which served as a practical use case for a design pattern which is often used in software development: the Data Transfer Object.
In the future, these applications can be extended using modern frameworks.
Here is some advice to continue improving your skills:
Thank you for completing all the tutorials. If you enjoyed them, please leave us a review on the contact page of our website.
Learn advanced concepts, work on real-world projects, and fast-track your journey to becoming a proficient Java developer. Start now and unlock your full potential in the world of Java programming!
Start now and unlock your full potential in the world of Java programming!


The place where you can start your Java journey.
© All Rights Reserved.