If in the past tutorials, we learned how to successfully manage the stocks, now it is time to create our lemonades. We need to analyze the problem and develop a solution to keep track of all our sales. In order to create a lemonade, we need to learn how to handle a new type of relationship between entities: many to many.

Let’s revisit the given problem:
…
Our application should be able to read a file containing a list of lemonades recipes, each made from a certain number and combination of products. Each type of lemonade will have a different name, a selling price and a list of required products.
…
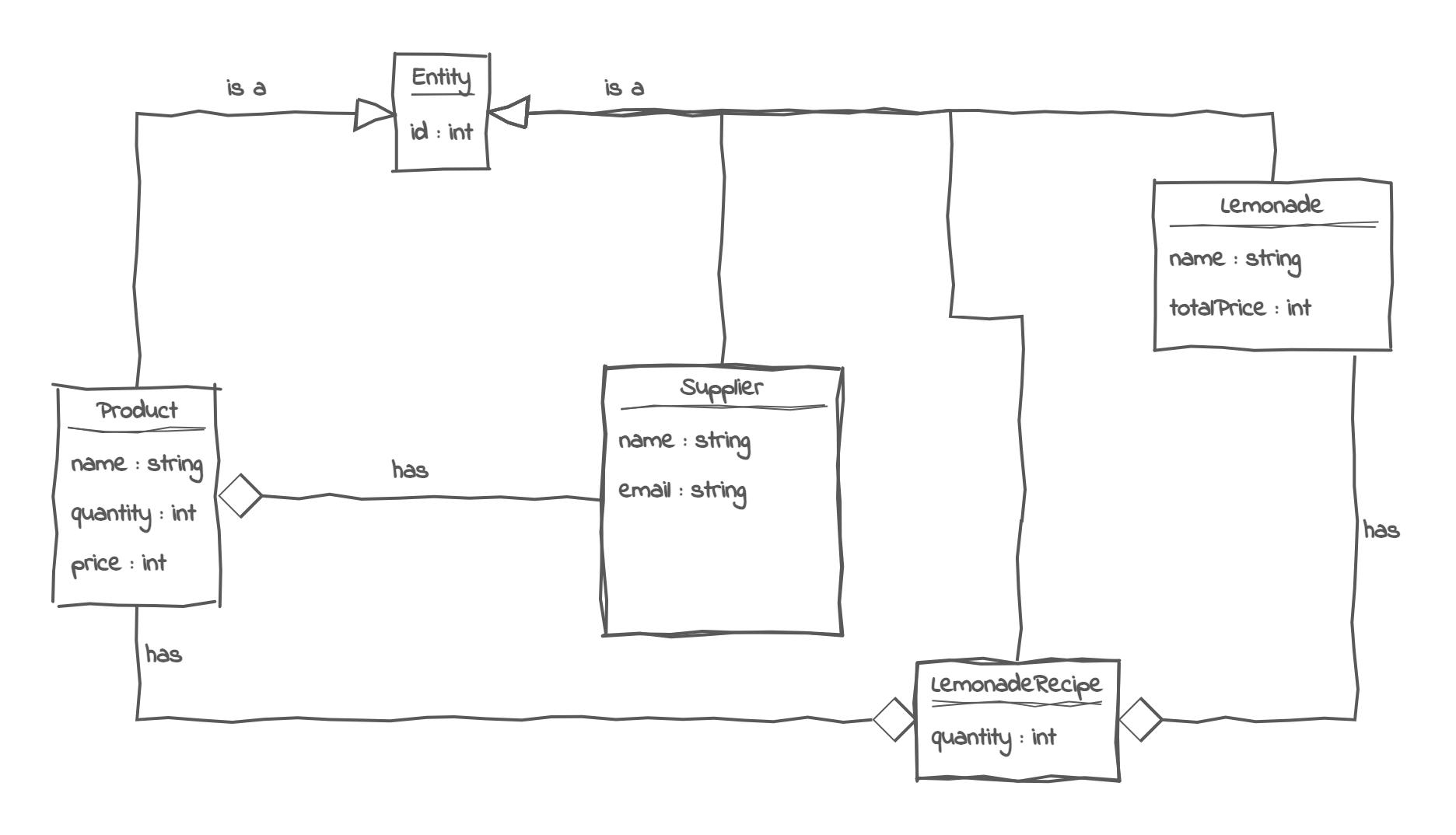
We need to create a class diagram for this part of the problem. We already have the products, and we now need to add a representation for lemonade. To do this, we need to create a new class, Lemonade, which has a name and a final price as attributes.
Each product can belong to multiple lemonades, which makes this a many-to-many relationship. This type of relationship is usually represented by creating a separate entity: LemonadeRecipe. This new entity will help us map which product belongs to which lemonade and in what quantity.
In other words, there is a one to many association between Lemonade and LemonadeRecipe, as well as a one to many association between LemonadeRecipe and Product. This design pattern provides the flexibility to track the quantity of products required for all lemonades.
The diagram would look like this:
First of all, we need to create Domain package classes, Lemonade and LemonadeRecipe:
public class Lemonade extends Entity {
private String name;
private String totalPrice;
public Lemonade(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getTotalPrice() {
return totalPrice;
}
public void setTotalPrice(String totalPrice) {
this.totalPrice = totalPrice;
}
}
And the mapping class: LemonadeRecipe:
public class LemonadeRecipe extends Entity {
private Product product;
private Lemonade lemonade;
private int quantity;
public LemonadeRecipe(Product product, Lemonade lemonade, int quantity) {
this.product = product;
this.lemonade = lemonade;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
...
// getters and setters
}
Then, we need to implement repositories for each class.
If we were only using the memory storage, we could use the GenericRepository. However, since we need to store our lemonades in files, we require special repositories with methods for read and write in file for each entity.
Let’s consider how we can store our data. First, we need a file for our lemonades. An example of the file can be:
1,The healthier lemonade,12
2,Cold and fresh,10
And then an example for LemonadeRecipe, where each line has the following structure: (leomnadeRecipeId, productId, lemonadeId, quantity) :
1,1,1,2
1,2,1,2
2,3,2,5
2,2,3,3
Next, we create the Repositories based on our previous examples for each class.
public class LemonadeRecipeFileRepository extends GenericRepository<LemonadeRecipe> {
private String filename;
public LemonadeRecipeFileRepository(String filename) throws IDNotUniqueException {
super();
this.filename = filename;
loadLemonadesFromFile();
}
@Override
public LemonadeRecipe save(LemonadeRecipe lemonadeRecipe) throws IDNotUniqueException {
LemonadeRecipe savedLemonadeRecipe = super.save(lemonadeRecipe);
writeToFile();
return savedLemonadeRecipe;
}
@Override
public LemonadeRecipe update(LemonadeRecipe lemonade) {
LemonadeRecipe savedLemonade = super.update(lemonade);
writeToFile();
return savedLemonade;
}
@Override
public void delete(int lemonadeId) {
super.delete(lemonadeId);
writeToFile();
}
public List<LemonadeRecipe> readLemonadesRecipesFromFile() {
List<LemonadeRecipe> lemonadeRecipes = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] elems = line.split(",");
int id = Integer.parseInt(elems[0]);
int productId = Integer.parseInt(elems[1]);
int lemonadeId = Integer.parseInt(elems[2]);
int quantity = Integer.parseInt(elems[3]);
Product product = new Product(productId);
Lemonade lemonade = new Lemonade(lemonadeId);
LemonadeRecipe lemonadeRecipe = new LemonadeRecipe(id, product, lemonade, quantity);
lemonadeRecipes.add(lemonadeRecipe);
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return lemonadeRecipes;
}
private void loadLemonadesFromFile() throws IDNotUniqueException {
List<LemonadeRecipe> lemonadeRecipes = readLemonadesRecipesFromFile();
for (LemonadeRecipe lemonadeRecipe : lemonadeRecipes) {
this.save(lemonadeRecipe);
}
}
private void writeToFile() {
BufferedWriter writer = null;
try {
writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filename));
Iterable<LemonadeRecipe> lemonadeRecipes = findAll();
for (LemonadeRecipe lemonadeRecipe : lemonadeRecipes) {
String line = lemonadeRecipe.getId() + "," + lemonadeRecipe.getProduct().getId() + "," + lemonadeRecipe.getLemonade().getId() + "," + lemonadeRecipe.getQuantity();
writer.write(line);
writer.newLine();
}
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public class LemonadeFileRepository extends GenericRepository<Lemonade> {
private String filename;
public LemonadeFileRepository(String filename) throws IDNotUniqueException {
super();
this.filename = filename;
loadLemonadesFromFile();
}
@Override
public Lemonade save(Lemonade lemonade) throws IDNotUniqueException {
Lemonade savedLemonade = super.save(lemonade);
writeToFile();
return savedLemonade;
}
@Override
public Lemonade update(Lemonade lemonade) {
Lemonade savedLemonade = super.update(lemonade);
writeToFile();
return savedLemonade;
}
@Override
public void delete(int lemonadeId) {
super.delete(lemonadeId);
writeToFile();
}
public List<Lemonade> readLemonadesFromFile() {
List<Lemonade> lemonades = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] elems = line.split(",");
int id = Integer.parseInt(elems[0]);
String name = elems[1];
int totalPrice = Integer.parseInt(elems[2]);
Lemonade lemonade = new Lemonade(id, name, totalPrice);
lemonades.add(lemonade);
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return lemonades;
}
private void loadLemonadesFromFile() throws IDNotUniqueException {
List<Lemonade> lemonades = readLemonadesFromFile();
for (Lemonade lemonade : lemonades) {
this.save(lemonade);
}
}
private void writeToFile() {
BufferedWriter writer = null;
try {
writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filename));
Iterable<Lemonade> lemonades = findAll();
for (Lemonade lemonade : lemonades) {
String line = lemonade.getId() + "," + lemonade.getName() + "," + lemonade.getTotalPrice();
writer.write(line);
writer.newLine();
}
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
In the Service Layer, we only need to add a LemonadeService. This will include a method for retrieving all the lemonades and obtaining the recipe for a specific lemonade. We need to add the newly created repositories as attributes, and the ProductService.
public class LemonadeService {
private RepositoryInterface<LemonadeRecipe> lemonadeRecipeRepository;
private RepositoryInterface<Lemonade> lemonadeRepository;
private ProductService productService;
public LemonadeService(RepositoryInterface lemonadeRecipeRepository, RepositoryInterface lemonadeRepository, ProductService productService) {
this.lemonadeRepository = lemonadeRepository;
this.lemonadeRecipeRepository = lemonadeRecipeRepository;
this.productService = productService;
}
...
}
The final class will look like this:
public class LemonadeService {
private RepositoryInterface<LemonadeRecipe> lemonadeRecipeRepository;
private RepositoryInterface<Lemonade> lemonadeRepository;
private ProductService productService;
public LemonadeService(RepositoryInterface lemonadeRecipeRepository, RepositoryInterface lemonadeRepository, ProductService productService) {
this.lemonadeRepository = lemonadeRepository;
this.lemonadeRecipeRepository = lemonadeRecipeRepository;
this.productService = productService;
}
public Lemonade findById(int lemonadeId) {
return lemonadeRepository.findById(lemonadeId);
}
public Iterable<Lemonade> findAll() {
return lemonadeRepository.findAll();
}
public List<LemonadeRecipe> findLemonadeRecipe(int lemonadeId) {
Iterable<LemonadeRecipe> allLemonadeRecipes = lemonadeRecipeRepository.findAll();
List<LemonadeRecipe> recipeForTheRequestedLemonade = new ArrayList<>();
for (LemonadeRecipe lemonadeRecipe : allLemonadeRecipes) {
if (lemonadeRecipe.getLemonade().getId() == lemonadeId) {
Product loadedProduct = productService.findById(lemonadeRecipe.getProduct().getId());
lemonadeRecipe.setProduct(loadedProduct);
recipeForTheRequestedLemonade.add(lemonadeRecipe);
}
}
return recipeForTheRequestedLemonade;
}
}
Finally, we need to update the class used for the UI:
public class UserInterface {
private ProductService productService;
private SupplierService supplierService;
private LemonadeService lemonadeService;
private OrderService orderService;
public UserInterface(ProductService productService, SupplierService supplierService, LemonadeService lemonadeService, OrderService orderService) {
this.productService = productService;
this.supplierService = supplierService;
this.lemonadeService = lemonadeService;
this.orderService = orderService;
}
private void showMenu() {
System.out.println("Welcome to the Lemonade Stand Administration App.");
System.out.println("The Menu:");
System.out.println("1. Manage suppliers");
System.out.println("2. Manage products");
System.out.println("3. Manage lemonades recipes");
System.out.println("4. Create an order");
System.out.println("5. Daily sales report");
System.out.println("6. Empty products stock report");
System.out.println("7. Exit");
System.out.println("What do you want to do? ");
}
private void showSuppliersMenu() {
System.out.println("Welcome to the Lemonade Stand Administration App.");
System.out.println("The Suppliers menu:");
System.out.println("1. Add a supplier");
System.out.println("2. Update a supplier");
System.out.println("3. Remove a supplier");
System.out.println("4. Display all suppliers");
System.out.println("5. Back to main menu");
System.out.println("What do you want to do? ");
}
private void showProductsMenu() {
System.out.println("Welcome to the Lemonade Stand Administration App.");
System.out.println("The Product menu:");
System.out.println("1. Add a product");
System.out.println("2. Update a product");
System.out.println("3. Remove a product");
System.out.println("4. Display all products");
System.out.println("5. Back to main menu");
System.out.println("What do you want to do? ");
}
private void showLemonadesMenu() {
System.out.println("Welcome to the Lemonade Stand Administration App.");
System.out.println("The Lemonade menu:");
System.out.println("1. Display all lemonades");
System.out.println("2. Display the recipe for a lemonade");
System.out.println("3. Exit");
System.out.println("What do you want to do? ");
}
public void runMenu() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int option = -1;
while (option != 7) {
showMenu();
option = scanner.nextInt();
switch (option) {
case 1:
runSuppliersMenu(scanner);
break;
case 2:
runProductsMenu(scanner);
break;
case 3:
runLemonadesMenu(scanner);
break;
case 4:
runOrderOption(scanner);
break;
case 5:
runDailyReportOption();
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("Not implemented yet!");
break;
case 7:
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
public void runDailyReportOption() {
System.out.println("You want to create a daily report.");
List<DailySalesDTO> report = orderService.getDailyReport();
for(DailySalesDTO day: report){
String reportLine = "For the day %s the total value of the sells is %d.";
String reportLineFormatted = String.format(reportLine, day.getDayString(), day.getTotalSales());
System.out.println(reportLineFormatted);
}
}
public void runOrderOption(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.println("You want to create a new order.");
System.out.print("Order id: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Lemonade id: ");
int lemonadeId = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Quantity: ");
int quantity = scanner.nextInt();
try {
Order order = orderService.saveOrder(id, lemonadeId, quantity);
System.out.printf("The order with ID=%s has been saved \n", order.getId());
} catch (ValidationException | IDNotUniqueException e) {
System.out.println("Error with saving the order: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public void runLemonadesMenu(Scanner scanner) {
int option = -1;
while (option != 3) {
showLemonadesMenu();
option = scanner.nextInt();
switch (option) {
case 1:
handleShowLemonades();
break;
case 2:
handleShowLemonadeRecipes(scanner);
break;
case 3:
break;
}
}
}
public void runProductsMenu(Scanner scanner) {
int option = -1;
while (option != 5) {
showProductsMenu();
option = scanner.nextInt();
switch (option) {
case 1:
handleAddProduct(scanner);
break;
case 2:
handleRemoveProducts(scanner);
break;
case 3:
handleUpdateProduct(scanner);
break;
case 4:
handleShowProducts();
break;
case 5:
break;
}
}
}
public void runSuppliersMenu(Scanner scanner) {
int option = -1;
while (option != 5) {
showSuppliersMenu();
option = scanner.nextInt();
switch (option) {
case 1:
handleAddSupplier(scanner);
break;
case 2:
handleRemoveSuppliers(scanner);
break;
case 3:
handleUpdateSupplier(scanner);
break;
case 4:
handleShowSuppliers();
break;
case 5:
break;
}
}
}
private void handleAddSupplier(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.print("ID: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Name: ");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("Contact email: ");
String contactEmail = scanner.next();
try {
Supplier savedSupplier = supplierService.saveSupplier(id, name, contactEmail);
System.out.printf("The supplier with ID=%s has been saved \n", savedSupplier.getId());
} catch (ValidationException | IDNotUniqueException e) {
System.out.println("Error with saving the supplier: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void handleUpdateSupplier(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.print("The ID of the supplier to be updated: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("New name: ");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("New contact email: ");
String contactEmail = scanner.next();
Supplier updatedSupplier = supplierService.updateSupplier(id, name, contactEmail);
System.out.printf("The supplier with ID=%s has been updated \n", updatedSupplier.getId());
}
private void handleRemoveSuppliers(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.print("The ID of the supplier to be removed: ");
int supplierIdToRemove = scanner.nextInt();
supplierService.removeSupplier(supplierIdToRemove);
System.out.printf("The product with ID=%s has been removed \n", supplierIdToRemove);
}
private void handleShowSuppliers() {
Iterable<Supplier> supplierList = supplierService.findAll();
displaySuppliers(supplierList);
}
private void displaySuppliers(Iterable<Supplier> suppliers) {
for (Supplier supplier : suppliers) {
System.out.println(supplier);
}
}
private void handleShowLemonades() {
Iterable<Lemonade> lemonades = lemonadeService.findAll();
for (Lemonade lemonade : lemonades) {
System.out.println(lemonade);
}
}
private void handleShowLemonadeRecipes(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.print("The ID of the lemonade: ");
int lemonadeId = scanner.nextInt();
List<LemonadeRecipe> requestedLemonadeRecipe = lemonadeService.findLemonadeRecipe(lemonadeId);
System.out.println("The requested lemonade contains: ");
for (LemonadeRecipe lemonadeRecipe : requestedLemonadeRecipe) {
System.out.println("The product " + lemonadeRecipe.getProduct().getName() + " with quantity of " + lemonadeRecipe.getQuantity());
}
}
private void handleAddProduct(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.print("ID: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Name: ");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("Description: ");
String description = scanner.next();
System.out.print("Price: ");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Quantity: ");
int quantity = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Supplier id: ");
int supplierId = scanner.nextInt();
try {
productService.saveProduct(id, name, description, price, quantity, supplierId);
} catch (ValidationException | IDNotUniqueException e) {
System.out.println("Error with saving the product: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void handleRemoveProducts(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.print("The ID of the product to be removed: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
productService.removeProduct(id);
}
private void handleUpdateProduct(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.print("The ID of the product to be updated: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("New name: ");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("New description: ");
String description = scanner.next();
System.out.print("New price: ");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("New quantity: ");
int quantity = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Supplier id: ");
int supplierId = scanner.nextInt();
try {
productService.updateProduct(id, name, description, price, quantity, supplierId);
} catch (ValidationException e) {
System.out.println("Error with saving the product: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void handleShowProducts() {
Iterable<Product> productList = productService.getAll();
for (Product product : productList) {
System.out.println(product);
}
}
}
Create a new menu item to display the lemonades that are out of stock. You can use the LemonadeRecipe to determine the products and if any product has insufficient stock (this means that the lemonade is unavailable).
Which layer should be updated with a new method for this type of filtering?
In this tutorial, we learned how to handle a new type of relationship between entities. We successfully created the mechanism required to create a lemonade. Next time, we will create an order to track all our sales.
Learn advanced concepts, work on real-world projects, and fast-track your journey to becoming a proficient Java developer. Start now and unlock your full potential in the world of Java programming!
Start now and unlock your full potential in the world of Java programming!


The place where you can start your Java journey.
© All Rights Reserved.